If you are searching for a new router then you must have come across these two terms 2.4GHz and 5GHz. These are frequency bands and this is how your data is transmitted from your router to your devices. So depending your need you may pick one over the other. In this article we’ll explain these two in simple terms to help you understand and choose your perfect router.
2.4GHz vs. 5GHz – At a Glance
(Brief Overview)
The main difference between 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands is the range (coverage) and the speed (bandwidth) that these bands provide. 2.4GHz band have longer range, but it transfer the data slower speeds. Instead, 5GHz bands have less range but have higher data rate (speed).
2.4GHz vs. 5GHz – Differences
(Explained)
We’ll compare these two bands according to the following parameters.
Range
The 2.4GHz frequency band covers a larger area and provides a more extended range than the 5GHz band. 5GHz band provides a comparatively smaller coverage area than the 2.4 GHz band. This is because when frequency increases, its ability to penetrate solid objects (like walls) decreases, reason why the 5GHz band was used mostly in outdoor deployments at the beginning. But at the same time, the higher the frequency, the faster the data is transmitted. Therefore, the 5GHz band carries more data and sends it faster.
If your priority is to provide an excellent Wi-Fi speed performance, your choice should lean to the 5GHz band, instead.
Signal Strength
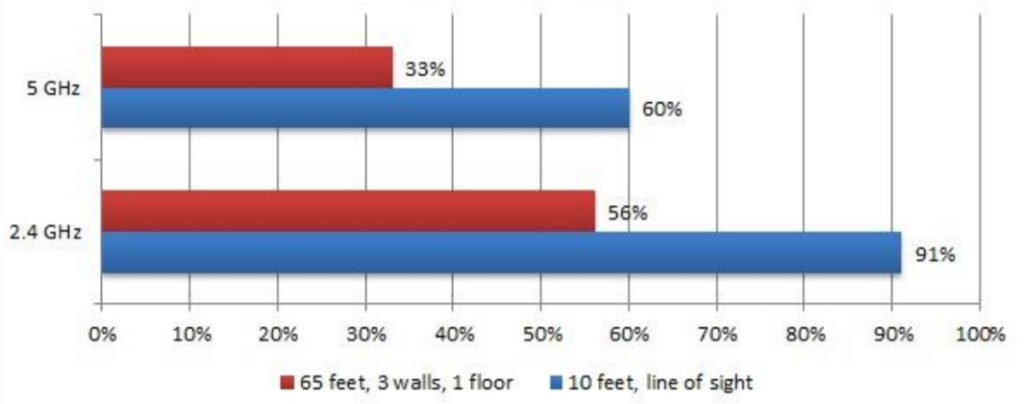
Speed
The 5GHz band offer greater speed as compared to 2.4GHz band, but in short range. But that is not the end of the story. There are other factors as well which determines your real world speed. Most of the time the speeds which are written in the box are just theoretical speed. These are tested in labs with ideal conditions. They don’t take real word factors like signal loss, physical obstruction etc. which leads to reduction in overall speed. Below is a comparison of theoretical and real-world speed of different bands with respective protocols.
| Frequency Bands | Ideal Speed | Real-World Speed |
|---|---|---|
| 2.4 GHz (802.11b) | 11 Mbps | 2-3 Mbps |
| 2.4 GHz (802.11g) | 54 Mbps | 10 -29 Mbps |
| 2.4 GHz (802.11n) | 300 Mpbs | 150 Mbps |
| 5 GHz (802.11a) | 6-54 Mbps | 3 – 32 Mbps |
| 5 GHz (802.11ac) | 433 Mbps – 1.7 Gbps | 210 Mbps – 1 G |
| 5 GHz (802.11n) | 900 Mbps | 450Mbps |
Apart from this, congestion in network also plays a vital role in speed fluctuations.
For instance, the 2.4GHz band usually supports 300Mbps, depending on the device type, however as so many devices use the 2.4GHz band, the resulting congestion can cause discontinued connections and slower speeds.
Instead, the 5GHz band can reach speeds of 1200Mbps or more depending on it’s wireless standard protocols (i.e., 802.11b, 802.11g, 802.11n, or 802.11ac). It tends to be less overcrowded than the 2.4GHz band because fewer devices use it and because it has more channels for devices to use than the 2.4GHz.
Price
Generally the 5GHz routers are far more expensive that 2.4GHz ones. If you are a light user and your maximum ISP speed is less than 100Mbps then it’s better to stick to 2.4GHz.
But if you are a gamer who need the lowest latency possible or you live in apartments surrounded by people, then to get uninterrupted connection you can go for 5GHz band.
Congestion
A lot of electronic devices and appliances use the 2.4 GHz frequency, including microwaves, baby monitors, and garage door openers. If you have many such appliances in your home, or if you live in apartments or condos surrounded by other people, then 2.4 GHz band is likely to be congested, which can damage speed and signal quality.
When to Choose 5GHz
If your device doesn’t need to be moved around much and can be located near your router, 5 GHz is your best choice to reduce congestion and take advantage of higher speeds. Similarly, if you’re doing a lot of high-bandwidth activities online, such as gaming or videoconferencing, it’s best to use this frequency and move as close as possible to the router. (Better yet, plug directly into the modem with an Ethernet cable if possible, as a wired connection is always more stable and faster than wireless.)
When to Choose 2.4GHz
Go for 2.4GHz if your device moves around a lot throughout the day (like your smartphone), especially if you have a large home, the 2.4 GHz frequency is your best bet. Wavelength of 2.4GHz is longer and can penetrate solid objects more easily than the 5 GHz band, making it ideal for devices that are taken from room to room or are more distant from the router.
